
Logout
If you want to log out click in LogOut


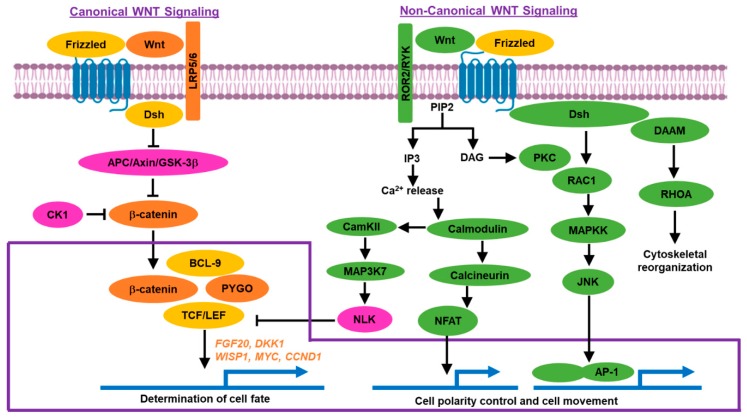
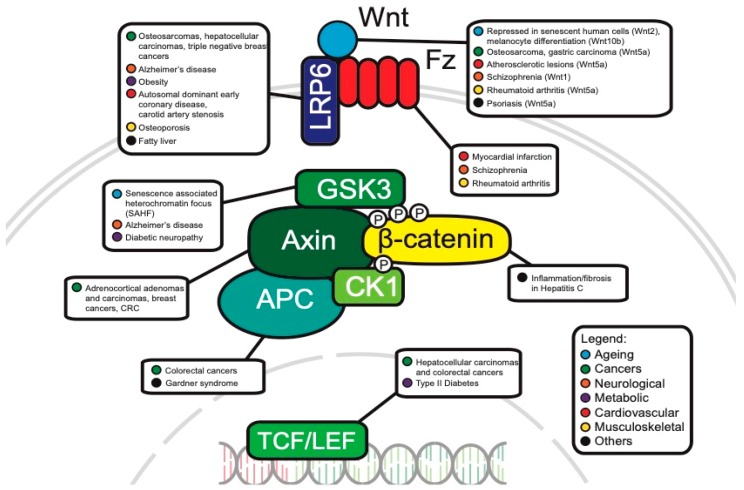
The WNT beta catenin signaling pathway is an evolutionarily conserved signal transduction pathway that regulates a wide range of cellular functions like differentiation, proliferation, embryonic growth, stem cell development, immune cell functions, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), metabolism, cell fate and tissue repair and regeneration (1,2).
You can custom your own SignArrays® with the genes of interest of your choice, according to your project, you just have to download and complete our Personalized SignArrays® information file and send it at contact@anygenes.com