
Logout
If you want to log out click in LogOut


The AMPK signaling pathway, with its highly conserved and adaptive enzyme complex 5′-Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase, plays a key role in cellular and systemic energy homeostasis (1).
AMPK supports numerous processes required for energy and redox homeostasis, including mitochondrial biogenesis, autophagy, glucose and lipid metabolism, TCA cycle, cell cycle progression (1,2). Activation of AMPK is regulated by diverse physiological and pathological conditions such as metabolic stress, caloric restriction, exercise, aging and obesity (2).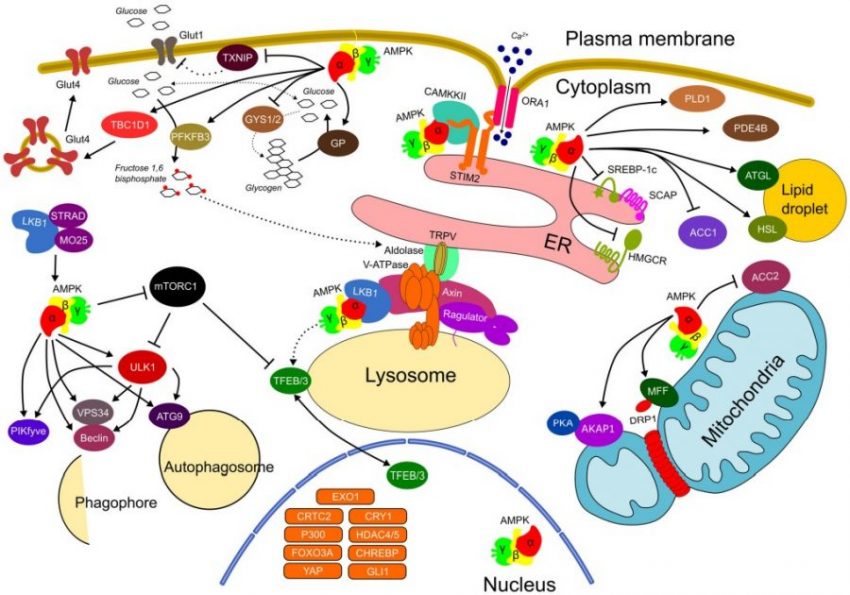
You can custom your own SignArrays® with the genes of interest of your choice, according to your project, you just have to download and complete our Personalized SignArrays® information file and send it at contact@anygenes.com