
Logout
If you want to log out click in LogOut


The function of the nitric oxide pathway is dependent on nitric oxide (NO), a potent signaling molecule. This pathway is essential for the regulation of various cellular processes in both healthy and diseased states. These processes include immune response, heart function, reproduction, muscle control, and nervous system activity. Additionally, the pathway is also responsible for vasodilation, neurotransmission, cell movement, and programmed cell death.
NO exerts numerous effects on the kidneys, heart and vasculature as well as on peripheral metabolically active organs (1,2,3).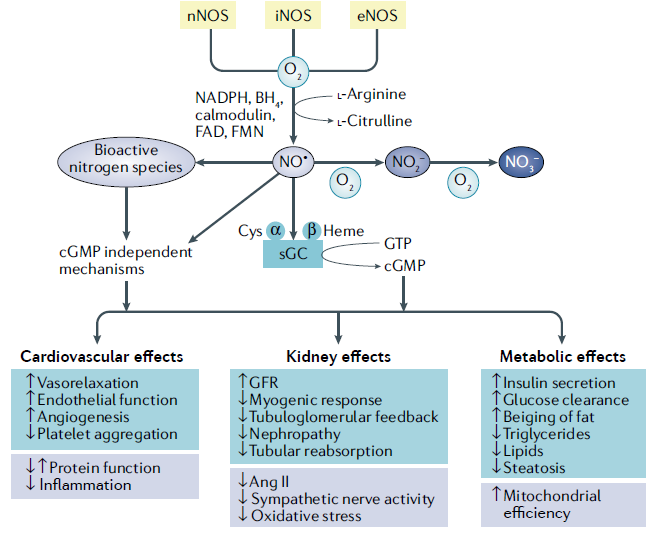
Various cells in the body produce NO internally through three different NOS systems. Neuronal NOS (nNOS or NOS1) and endothelial NOS (eNOS or NOS3) are consistently present. While inducible NOS (iNOS or NOS2) primarily links to inflammatory situations.
Neural NOS (nNOS) and endothelial NOS (eNOS) produce small amounts of NO. This, can act as a neurotransmitter, vasodilator, or assist in the release of insulin. While inducible NOS (iNOS) produces significant quantities of NO in order to fight against pathogens (2,5).
NO has a complex and multifaceted role in cancer (breast, lung, prostate, colon, gastric, pancreatic, ovarian, and neuroblastoma), aging, cardiovascular pathogenesis, ocular hypertension, Glaucoma … (3,4,5,6).
You can custom your own SignArrays® with the genes of interest of your choice, according to your project, you just have to download and complete our Personalized SignArrays® information file and send it at contact@anygenes.com