(1) Pruchniak MP, Aražna M & Demkow U. Biochemistry of Oxidative Stress. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2016) 878:9-19.
(2) Ihsan AU & al. Role of oxidative stress in pathology of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome and male infertility and antioxidants function in ameliorating oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother. (2018) 106:714-723.
(3) Peña-Oyarzun D & al. Autophagy and oxidative stress in non-communicable diseases: A matter of the inflammatory state?. Free Radic Biol Med. (2018) 20;124:61-78.
(4) Liguori I & al. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin Interv Aging. (2018) 26;13:757-772.
(5) Simioni C & al. Oxidative stress: role of physical exercise and antioxidant nutraceuticals in adulthood and aging. Oncotarget. (2018) 30; 9(24): 17181–17198.
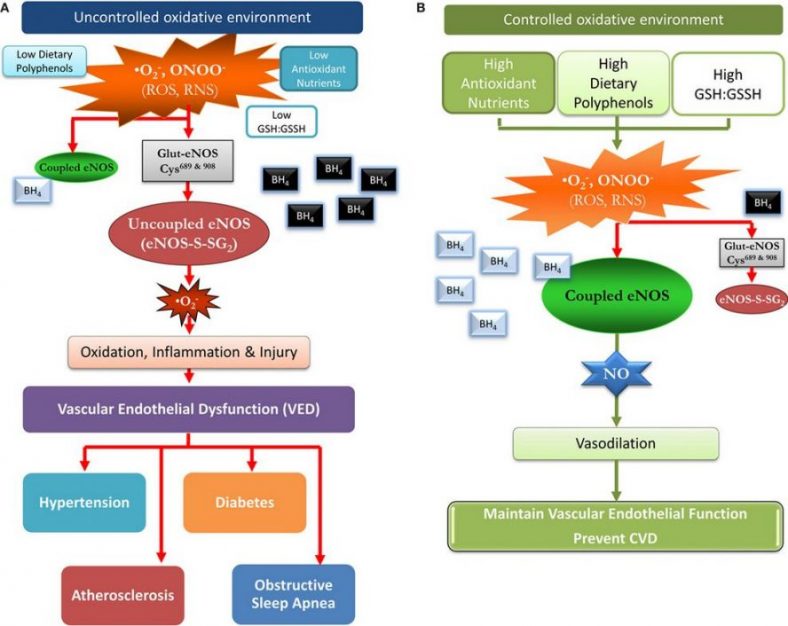
(6) Varadharaj S & al. Role of Dietary Antioxidants in the Preservation of Vascular Function and the Modulation of Health and Disease. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2017) 1;4:64.