
Logout
If you want to log out click in LogOut


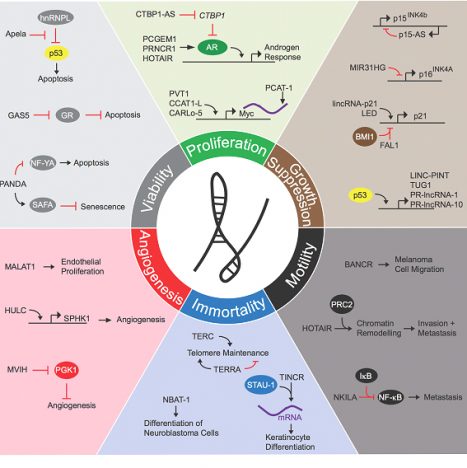
Long Non Coding RNA (LncRNAs) are RNAs that do not encode proteins and are constituted with more than 200 nucleotides. A large majority of the genome, about 98%, is considered noncoding. However, the ENCODE project states that 80% of the genome has a function. (1,2).
You can custom your own SignArrays® with the genes of interest of your choice, according to your project, you just have to download and complete our Personalized SignArrays® information file and send it at contact@anygenes.com