
Logout
If you want to log out click in LogOut


Transforming growth factor β (TGF beta) is a multi-functional secreted cytokine that plays pivotal roles in embryonic development and adult tissue maintenance (1), moreover it regulates numerous biological processes including promotion of cell differentiation and proliferation, control of cell apoptosis and cell cycle, regulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), angiogenesis, extracellular matrix (ECM) formation, suppression of immune response, and maintenance of genomic stability and stem cell homeostasis (2), (in blue among AnyGenes pathways).
It has been proved that TGFβ plays dual roles in tumor progression as tumor-promoter or suppressor. In an early stage, TGFβ inhibits cell proliferation and is involved in cell apoptosis. In an advanced tumor, TGFβ signaling pathway induces tumor invasion and metastasis through promoting angiogenesis, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, and immune escape (3).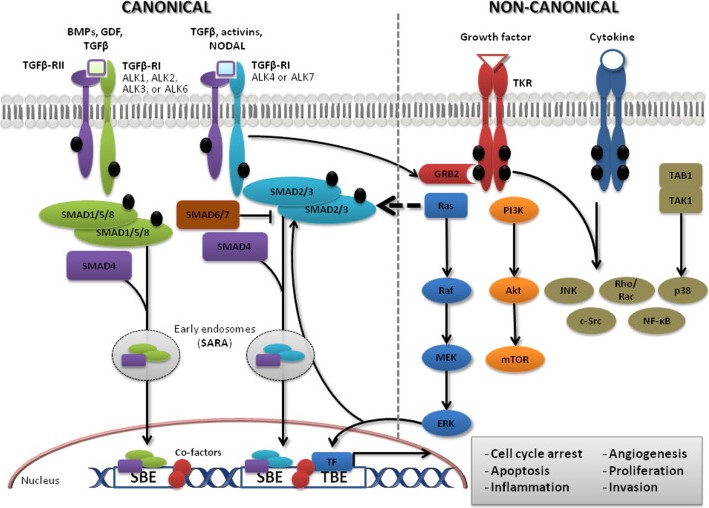
You can custom your own SignArrays® with the genes of interest of your choice, according to your project, you just have to download and complete our Personalized SignArrays® information file and send it at contact@anygenes.com