
Logout
If you want to log out click in LogOut


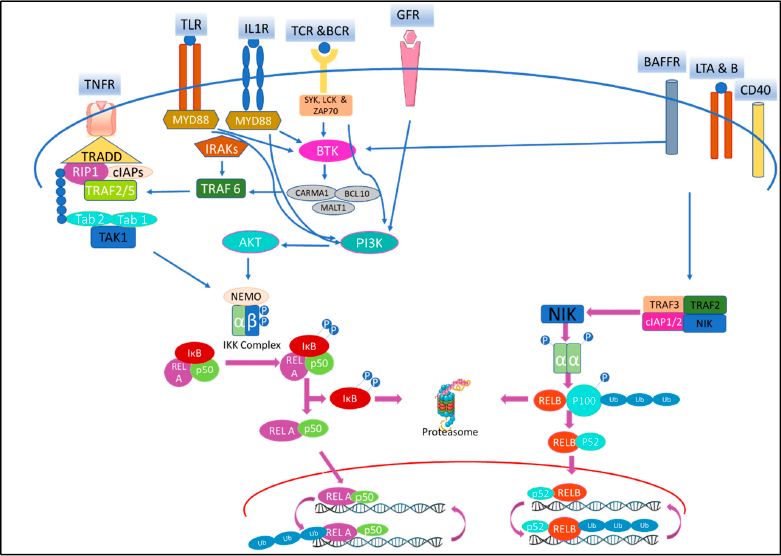
NFKB Pathway with its important nuclear transcription factor NF-κB, which plays a key regulatory role in innate immunity, acquired immunity, inflammatory response and the progression of tumors (1).
You can custom your own SignArrays® with the genes of interest of your choice, according to your project, you just have to download and complete our Personalized SignArrays® information file and send it at contact@anygenes.com