
Logout
If you want to log out click in LogOut


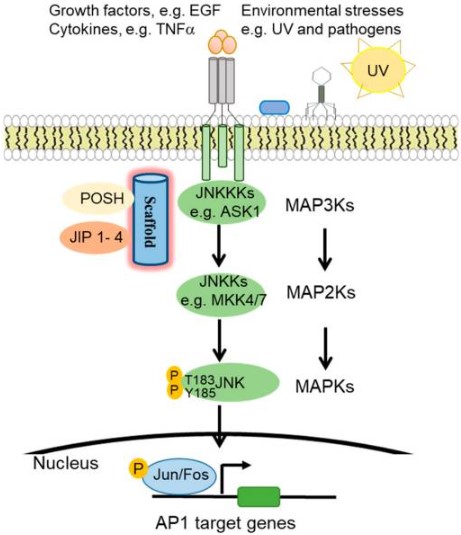
It is part of the canonical mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) family. These proteins are highly responsive to a diverse array of stress stimuli. This includes UV radiation, bacterial and viral infections, heat shock, and osmotic and genotoxic stresses.
c-Jun N-terminal kinases JNKs also known as stress-activated protein kinases (SAPK). This is due to its important role in the stress response.
Activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway depends largely on the context and duration of activation. Transient activation of JNK pathway could result in proliferation, whereas prolonged activation could trigger cell death.
In response to environmental stresses, growth factor, and cytokines, JNKKKs (JNK kinase kinases) like ASK1 phosphorylates JNKKs (JNK kinases). Then, the JNKKs activate JNK. Specifically, upstream MAPK2K (MKK4 and MKK7) activates JNK. This via phosphorylation of the threonine and tyrosine residues of the conserved ThrProTyr (TPY) motif.
Upon activation, JNK phosphorylates downstream target proteins. Among them activator of transcription factor-1 (AP1) protein family, activating transcription factors (ATF), and (ETS protein Like- 1) Elk1.(3,4).
There is evidence to suggest that this signaling pathway functions as both a tumor suppressor and a cancer promoter. This pathway may thus be a viable target for molecular cancer therapy because of its complex impact on cancer (2,3,4).
You can custom your own SignArrays® with the genes of interest of your choice, according to your project, you just have to download and complete our Personalized SignArrays® information file and send it at contact@anygenes.com