
Logout
If you want to log out click in LogOut


NLRP3 inflammasome is a multimeric cytosolic protein complex that assembles in response to cellular perturbations.
Activation of this complex is regulated through two-step process, with priming at the transcriptional and posttranslational levels (Signal 1) and assembly by multiple pathways in response to a variety of exogenous pathogen-derived or endogenous danger molecules (Signal 2). This assembly leads to the activation of caspase-1, which promotes maturation and release of the inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-18, as well as inflammatory cell death (pyroptosis) (1).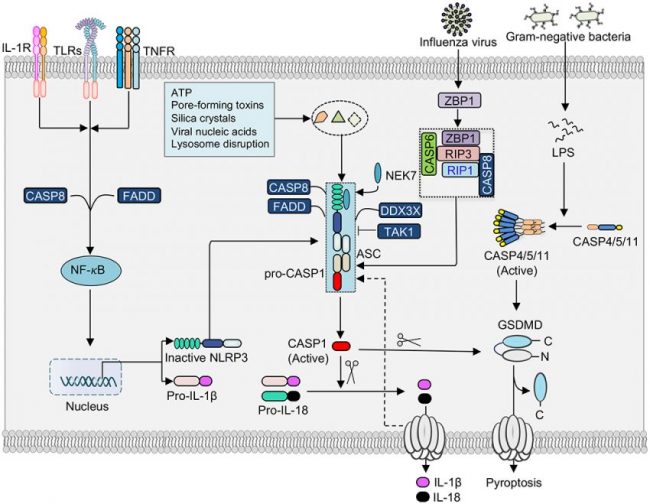
You can custom your own SignArrays® with the genes of interest of your choice, according to your project, you just have to download and complete our Personalized SignArrays® information file and send it at contact@anygenes.com