
Logout
If you want to log out click in LogOut


The JAK-STAT pathway, also called Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (JAK/STAT) signaling pathway, is a universally expressed intracellular signal transduction pathway. It plays a central role in many crucial biological processes, including immune responses, cell proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, apoptosis, survival...depending on the physiological signal.
This pathway play a pivotal role in the transfer of signals from cell membrane receptors to the nucleus (1,3).
Ligands, such as cytokines, growth hormone and factor, as well as their respective receptors, activates the JAK/STAT pathway. The activated JAKs phosphorylate the cytoplasmic tyrosine residues of the receptor. This creates binding sites for other signaling molecules that contain a Src homology 2 (SH2) domain, such as STATs. Then JAKs phosphorylate STATs.
Several molecules can negativly regulates jak stat pathway. Among them SOCS, protein inhibitor of activated STAT (PIAS) and protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) (2,3).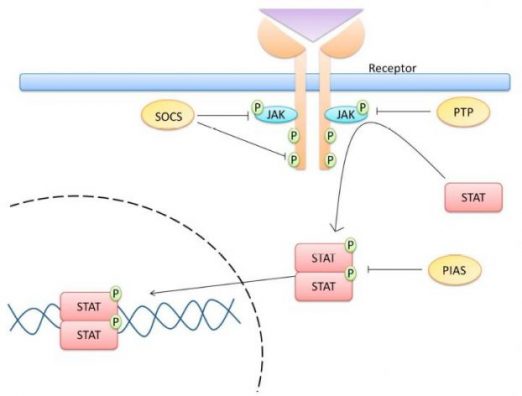
Besides its important impact in cellular signaling, the JAK/STAT pathway enters into several diseases. Among this Rheumatoid arthritis, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, sepsis, inflammatory bowel disease, COVID-19 infection... (1,2,4,5).
Aberrant JAK/STAT signaling contributes to cancer progression and metastatic development. This includes myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). In addition to other cancers in lung, gastric, prostate, colon, cervical, breast...... (1,3,5).You can custom your own SignArrays® with the genes of interest of your choice, according to your project, you just have to download and complete our Personalized SignArrays® information file and send it at contact@anygenes.com