
Logout
If you want to log out click in LogOut


Insulin resistance pathway (IR) refers to the body's resistance to the effects of insulin on glucose uptake, metabolism, or storage.
Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by the beta cells in the pancreas. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of glucose and lipids in the body.
Insulin signaling maintain glucose balance by reducing the production of glucose in the liver through decreased gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis. As a result, the uptake of glucose in muscle and fat tissues increases. Insulin is also essential for lipid metabolism, as it stimulates lipid production in both the liver and fat cells. This by inhibiting the release of fatty acids from triglycerides in muscle and fat tissues.
In normal conditions, increased plasma glucose levels lead to increased insulin secretion and circulating insulin levels. This stimulates glucose transfer into peripheral tissues and inhibiting hepatic gluconeogenesis.
The biological effects of insulin occur when it attaches to its membrane receptors, insulin receptor (INSR). This activation triggers specific adapter proteins like insulin receptor substrate (IRS), Src-homology 2 (SH2), protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B), PI3-kinase (PI3K), and different AKT isoforms. This initiates insulin signaling, leading to glucose homeostasis.Various factors, like changes in receptor expression, ligand binding, phosphorylation states, and kinase activity, contribute to the different characteristics of insulin receptor (IR) phenotypes.
Akt activation has multiple downstream targets that produce distinct signaling responses in target tissues. Among them, GLUT4, which facilitates glucose uptake in skeletal muscle and white adipose cells when stimulated by insulin (1).
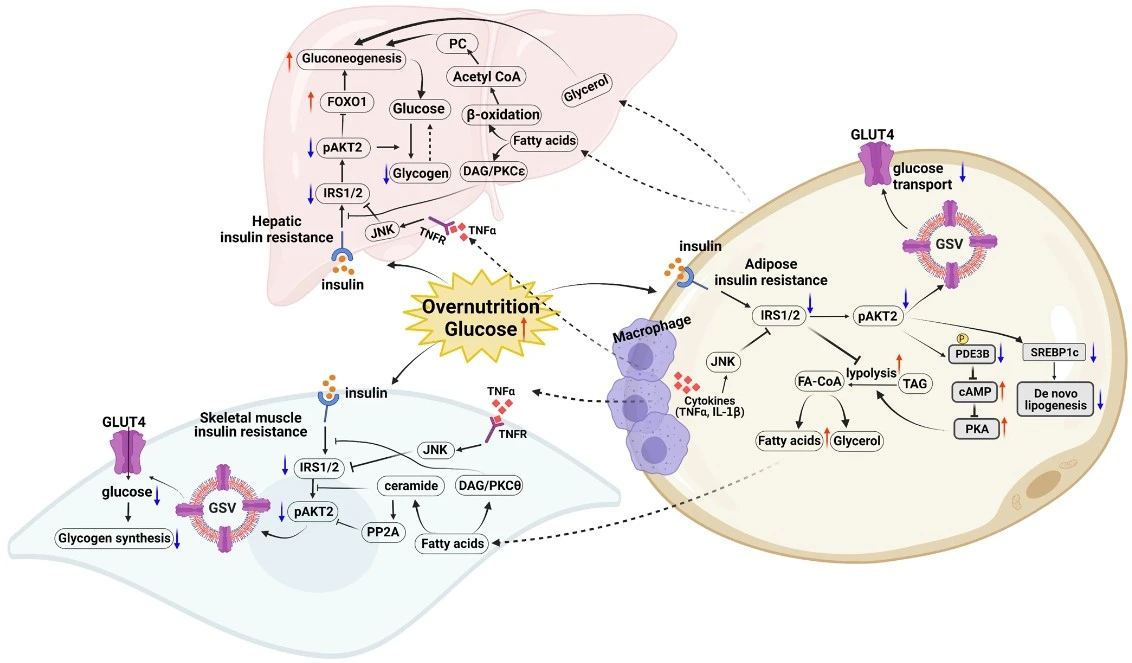
In human, insulin resistance associates with faulty insulin signaling. This occurs through various mechanisms. Including, storage of lipids, mitochondria dysfunction, and increased activity of stress-activated protein c-Jun-N-terminal-kinase (JNK). In addition to Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, Amino acids and Low-grade inflammation.
In addition to metabolites, other factors and circumstances that can lead to insulin resistance. They include cytokines and chemokines ( tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1β, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1). In addition to Adipokines(adiponectin, leptin, chemerin, resistin, visfatin and vaspin), myokines, hepatokines, microRNAs or exosomes (4).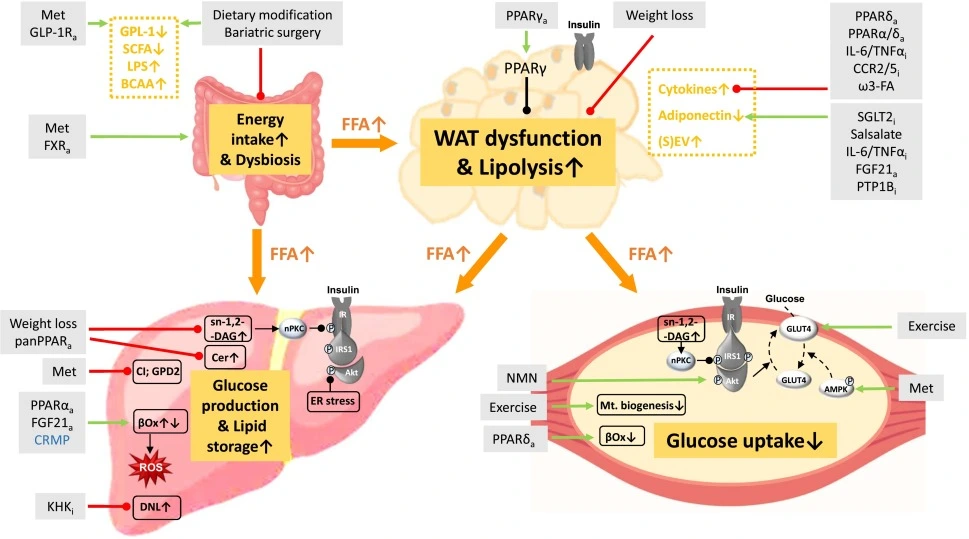
Insulin resistance (IR) occurs when the body requires higher levels of insulin than usual to achieve a normal response. This results in hyperinsulinemia and impaired glucose tolerance. This leads to various groups of disorders. Among them, obesity, diabetes, metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, heart disease, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and cancer..
Numerous studies have investigated the relationship between Alzheimer's disease and related disorders and insulin resistance in the brain and peripheral tissues (1,2).You can custom your own SignArrays® with the genes of interest of your choice, according to your project, you just have to download and complete our Personalized SignArrays® information file and send it at contact@anygenes.com