
Logout
If you want to log out click in LogOut


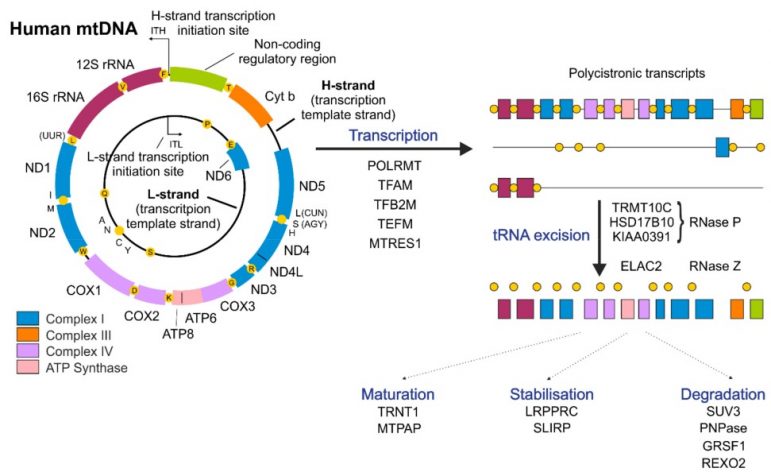
Human mitochondria with their own small circular genome (mtDNA) plays a central role in many processes such as ATP production, cell proliferation and regulating apoptosis processes, calcium buffering, ROS production, the biosynthesis of hormones and vitamins, inflammation …(1,2,4).
You can custom your own SignArrays® with the genes of interest of your choice, according to your project, you just have to download and complete our Personalized SignArrays® information file and send it at contact@anygenes.com